
Professionals are able to identify potential breathing complications (such as airway obstruction, hyperventilation, hypoventilation, or apnoea) and respond accordingly with a change in clinical management.
The wider use of EtCO 2 monitoring in different clinical areas reflects its importance as a monitoring tool that gives indication into three crucial aspects: the patient’s airway patency, breathing adequacy and circulatory status. House of Delegates of ASA (2011) “During moderate or deep sedation, the adequacy of ventilation shall be evaluated by continual observation of qualitative clinical signs and monitoring for the presence of exhaled carbon dioxide unless precluded or invalidated by the nature of the patient, procedure, or equipment.” 7ĪAGBI (2015) “Continuous capnography should be used for all patients undergoing moderate or deep sedation, and should be available wherever any patients undergoing anaesthesia or moderate or deep sedation are recovered.” 8

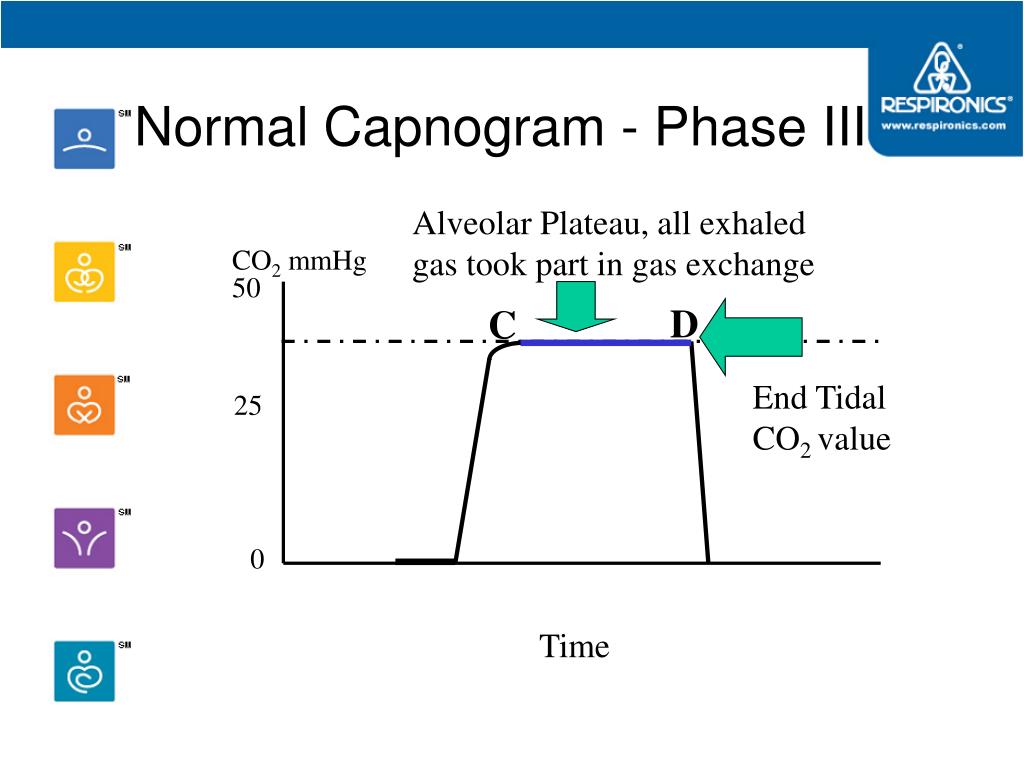
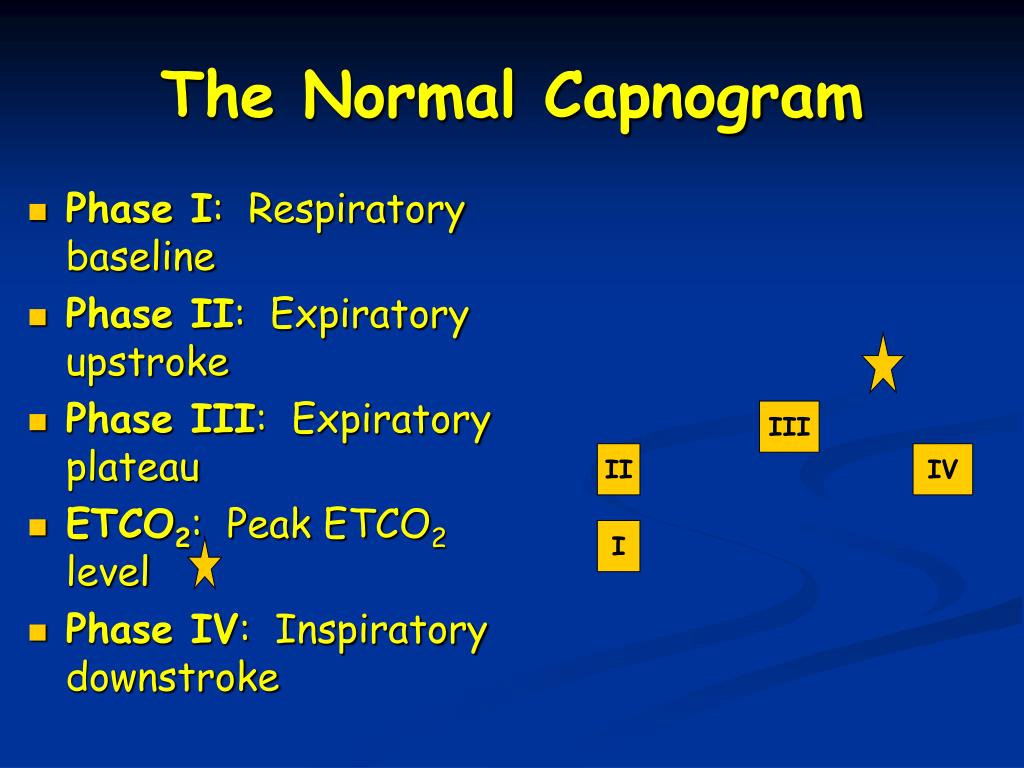
Several guidelines have supported the use of capnography outside the theatre environment:ĪLS Guidelines (2015) mention “Waveform capnography must be used to confirm and continually monitor tracheal tube placement, and may be used to monitor the quality of CPR and to provide an early indication of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC).” 6 The following image is taken from SedateUKĪlthough it has been historically used by anaesthetists during general anaesthesia, End Tidal CO 2 monitoring is becoming more common in other clinical areas like emergency environments, critical care, during sedation practice, in ambulatory settings and in post-operative recovery units. Phase IV: start of inhalation, CO 2 decreases to zero as atmospheric air enters the airway.This phase ends with a value of maximum CO 2 concentration Phase III: CO 2 concentration is relatively constant (reflects the concentration of CO 2 in the alveolar gas).Phase II: CO 2 increases rapidly as alveolar gas exits the airway.Phase I: start of exhalation, CO 2 concentration is initially zero.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
